深度学习概念梳理
本文介绍了深度学习中的一些概念,包括人工智能、机器学习、人工神经网络、深度学习、数据挖掘等,以及它们之间的相互关系。
人工智能
人工智能(英语:artificial intelligence,缩写为 AI)亦称智械、机器智能,指由人制造出来的机器所表现出来的智能。通常人工智能是指通过普通计算机程序来呈现人类智能的技术。该词也指出研究这样的智能系统是否能够實現,以及如何實現。同时,通过医学、神经科学、机器人学及统计学等的进步,常态预测则认为人类的很多职业也逐渐被其取代。
人工智能于一般教材中的定义领域是“智能主体(intelligent agent)的研究与设计”,智能主体指一个可以观察周遭环境并作出行动以达致目标的系统。约翰·麦卡锡于 1954 年的定义是“制造智能机器的科学与工程”。安德烈亚斯·卡普兰(Andreas Kaplan)和迈克尔·海恩莱因(Michael Haenlein)将人工智能定义为“系统正确解释外部数据,从这些数据中学习,并利用这些知识通过灵活适应实现特定目标和任务的能力”。
机器学习
机器学习是人工智能的一个分支。人工智能的研究历史有着一条从以“推理”为重点,到以“知识”为重点,再到以“学习”为重点的自然、清晰的脉络。显然,机器学习是实现人工智能的一个途径,即以机器学习为手段解决人工智能中的问题。机器学习在近 29 多年已发展为一门多领域交叉学科,涉及概率论、统计学、逼近论、凸分析、计算复杂性理论等多门学科。机器学习理论主要是设计和分析一些让计算机可以自动“学习”的算法。机器学习算法是一类从数据中自动分析获得规律,并利用规律对未知数据进行预测的算法。因为学习算法中涉及了大量的统计学理论,机器学习与推断统计学联系尤为密切,也被称为统计学习理论。算法设计方面,机器学习理论关注可以实现的,行之有效的学习算法。很多推论问题属于无程序可循难度,所以部分的机器学习研究是开发容易处理的近似算法。
机器学习已广泛应用于数据挖掘、计算机视觉、自然语言处理、生物特征识别、搜索引擎、医学诊断、检测信用卡欺诈、证券市场分析、DNA 序列测序、语音和手写识别、战略游戏和机器人等领域。
人工神经网络
人工神经网络(英语:Artificial Neural Network,ANN),简称神经网络(Neural Network,NN)或人工神經网络,在机器学习和认知科学领域,是一种模仿生物神经网络(动物的中枢神经系统,特别是大脑)的结构和功能的数学模型或计算模型,用于对函数进行估计或近似。神经网络由大量的人工神经元联结进行计算。大多数情况下人工神经网络能在外界信息的基础上改变内部结构,是一种自适应系统,通俗地讲就是具备学习功能。现代神经网络是一种非线性统计性数据建模工具,神经网络通常是通过一个基于数学统计学类型的学习方法(Learning Method)得以优化,所以也是数学统计学方法的一种实际应用,通过统计学的标准数学方法我们能够得到大量的可以用函数来表达的局部结构空间,另一方面在人工智能学的人工感知领域,我们通过数学统计学的应用可以来做人工感知方面的决定问题(也就是说通过统计学的方法,人工神经网络能够类似人一样具有简单的决定能力和简单的判断能力),这种方法比起正式的逻辑学推理演算更具有优势。
和其他机器学习方法一样,神经网络已经被用于解决各种各样的问题,例如机器视觉和语音识别。这些问题都是很难被传统基于规则的编程所解决的。
深度学习
深度学习(英语:deep learning)是机器学习的分支,是一种以人工神經网络为架构,对资料进行表征学习的算法。
深度学习是机器学习中一种基于对数据进行表征学习的算法。观测值(例如一幅图像)可以使用多种方式来表示,如每个像素强度值的向量,或者更抽象地表示成一系列边、特定形状的区域等。而使用某些特定的表示方法更容易从实例中学习任务(例如,人脸识别或面部表情识别)。深度学习的好处是用非监督式或半监督式的特征学习和分层特征提取高效算法来替代手工获取特征。
表征学习的目标是寻求更好的表示方法并创建更好的模型来从大规模未标记数据中学习这些表示方法。表示方法来自神经科学,并松散地创建在类似神经系统中的信息处理和对通信模式的理解上,如神经编码,试图定义拉动神经元的反应之间的关系以及大脑中的神经元的电活动之间的关系。
至今已有数种深度学习框架,如深度神经网络、卷积神经网络和深度置信网络和循环神经网络已被应用在计算机视觉、语音识别、自然语言处理、音频识别与生物信息学等领域并获取了极好的效果。
另外,“深度学习”已成为时髦术语,或者说是人工神经网络的品牌重塑。
数据挖掘(英语:data mining)是一个跨学科的计算机科学分支。它是用人工智能、机器学习、统计学和数据库的交叉方法在相对较大型的数据集中发现模式的计算过程。
数据挖掘过程的总体目标是从一个数据集中提取信息,并将其转换成可理解的结构,以进一步使用。除了原始分析步骤,它还涉及到数据库和数据管理方面、数据预处理、模型与推断方面考量、兴趣度度量、复杂度的考虑,以及发现结构、可视化及在线更新等后处理。数据挖掘是“数据库知识发现”(Knowledge-Discovery in Databases, KDD)的分析步骤,本质上属于机器学习的范畴。
相互关系
What’s The Difference Between AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning?
AI means getting a computer to mimic human behavior in some way.
Machine learning is a subset of AI, and it consists of the techniques that enable computers to figure things out from the data and deliver AI applications.
Deep learning, meanwhile, is a subset of machine learning that enables computers to solve more complex problems.
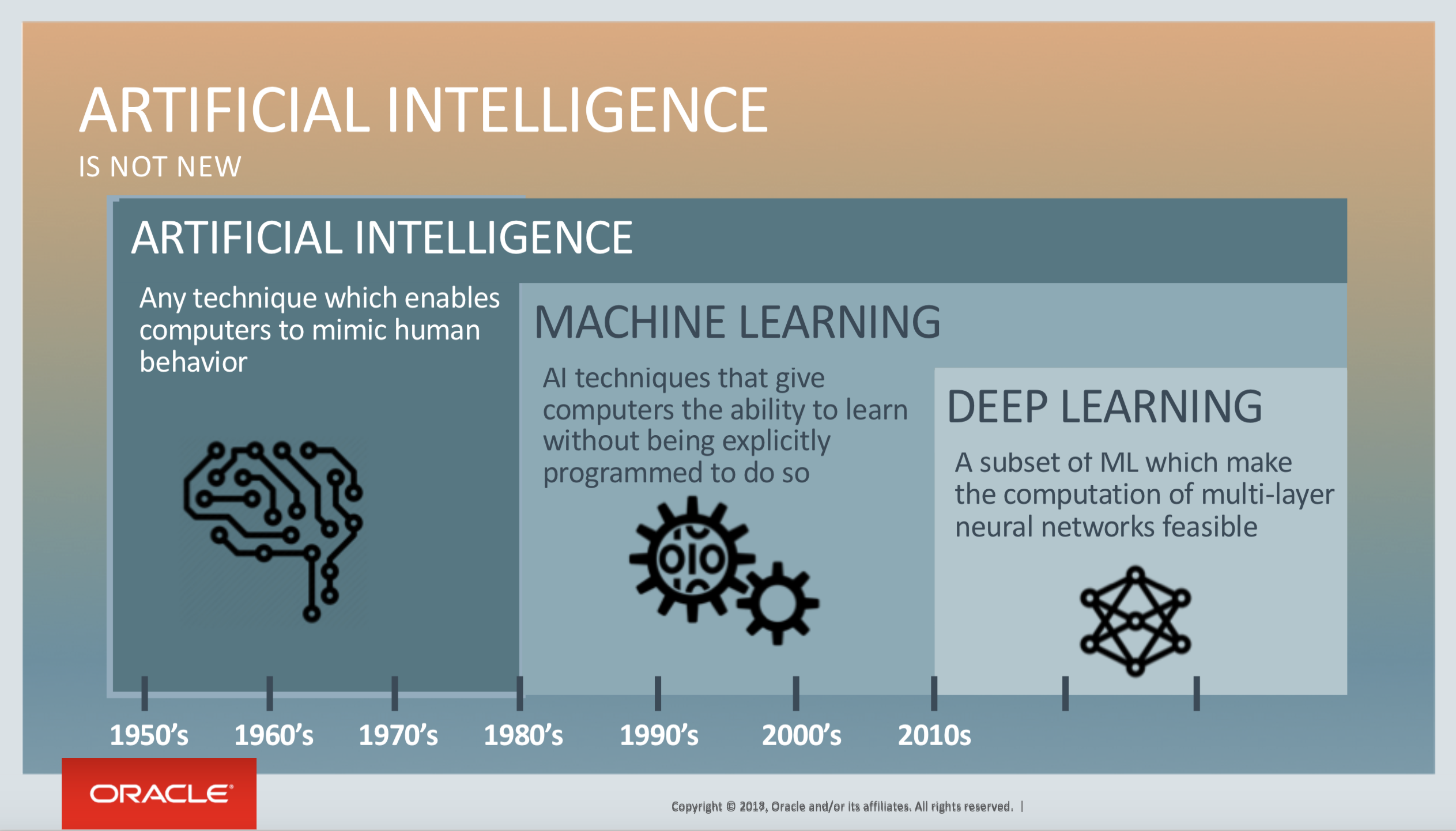
What’s the Difference Between AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning?
AI vs. Machine Learning vs. Deep Learning vs. Neural Networks: What’s the Difference?
Perhaps the easiest way to think about artificial intelligence, machine learning, neural networks, and deep learning is to think of them like Russian nesting dolls. Each is essentially a component of the prior term.
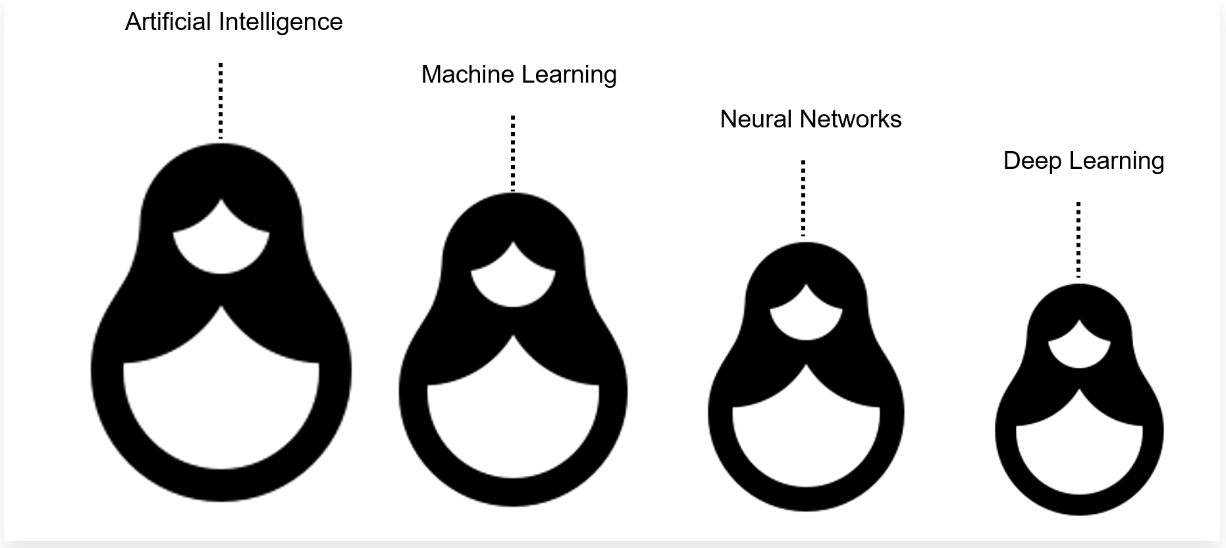
Artificial Intelligence
That is, machine learning is a subfield of artificial intelligence. Deep learning is a subfield of machine learning, and neural networks make up the backbone of deep learning algorithms. In fact, it is the number of node layers, or depth, of neural networks that distinguishes a single neural network from a deep learning algorithm, which must have more than three.
AI vs. Machine Learning vs. Deep Learning vs. Neural Networks: What’s the Difference?
Data Mining Vs. Machine Learning: What Is the Difference?
What is Data Mining?
Data mining is considered the process of extracting useful information from a vast amount of data. It’s used to discover new, accurate, and useful patterns in the data, looking for meaning and relevant information for the organization or individual who needs it. It’s a tool used by humans.
What is Machine Learning?
On the other hand, machine learning is the process of discovering algorithms that have improved courtesy of experience derived from data. It’s the design, study, and development of algorithms that permit machines to learn without human intervention. It’s a tool to make machines smarter, eliminating the human element (but not eliminating humans themselves; that would be wrong).
Difference Between Data mining and Machine learning:
Data mining is the subset of business analytics, it is similar to experimental research. The origins of data mining are databases, statistics. Whereas machine learning involves the algorithm that improves automatically through experience based on data.
Data Mining Vs. Machine Learning: What Is the Difference?
Data Mining vs Machine Learning
What’s More?
The main difference between regression and a neural network is the impact of change on a single weight. In regression, you can change a weight without affecting the other inputs in a function. However, this isn’t the case with neural networks. Since the output of one layer is passed into the next layer of the network, a single change can have a cascading effect on the other neurons in the network.

